
Visual learners prefer visual presentations of material – diagrams, charts, graphs, pictures. The visual/verbal scale: How do you prefer information to be presented? Visual They like discovering possibilities and relationships and working with ideas. They look at the big picture and try to grasp overall patterns. Intuitive learners prefer to take in information that is abstract, original, and oriented towards theory.


They are realistic and like practical applications. They are oriented towards details, facts, and figures and prefer to use proven procedures. Sensing learners prefer to take in information that is concrete and practical. The sensing/intuitive scale: How do you prefer to take in information? Sensing They prefer to think things through and understand things before acting. Reflective learners learn by thinking about information. They prefer to process information by talking about it and trying it out. The active/reflective scale: How do you prefer to process information? ActiveĪctive learners learn by doing something with information. Everyone uses all preferences at different times, but not usually with equal levels of confidence. Each of the four scales of the Soloman-Felder index of learning styles has two opposite preferences. The Soloman-Felder model of learning styles incorporates most of the major approaches to understanding learning preferences and is designed for use with college and university students to self-test their learning preferences. Learning style preferences refer to the “characteristic strengths and preferences in the ways take in and process information” (Felder, 1996).
#Aural learning style definition how to#
Furthermore, certain teaching strategies are best suited for all learners depending on the material that is being taught-learning how to make dilutions in a chemistry course, for example, requires a hands-on experiential approach, even if you have a preference to learn from reflection! Learning preferences In a recent study, Matching Learning Style to Instruction Method: Effects on Comprehension, Rogowsky and colleagues (2015) conducted an experimental test of the meshing hypothesis and found that matching the type of instruction to learning style did not make a difference on students’ comprehension of material. They state that while there have been studies done on how individuals can have preferences for learning, almost none of the studies employed rigourous research designs that would demonstrate that people benefit if they are instructed in a way that matches their learning style (Pashler, McDaniel, Roghrer, & Bjork, 2008).
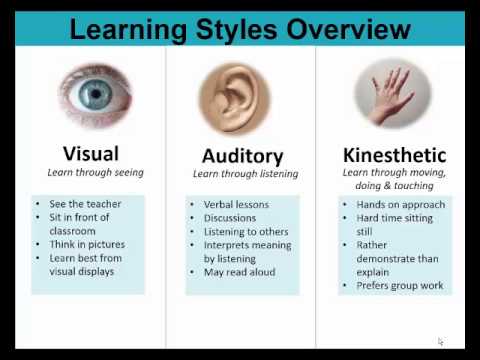

A group of psychologists reviewed the literature and in their report ( Learning Styles: Concepts and Evidence). However, there is virtually no evidence that supports that individuals have learning styles, nor that when taught in a way that “meshes” with their learning style that there is greater learning. There are many different theories of learning styles, including ones that classify people as visual, auditory, or tactile learners, or ones that outline different cognitive approaches people take in their learning. This Teaching Tip discusses the distinction between learning styles and learning preferences, and summarizes the Solomon-Felder index of learning styles. The idea of learning styles began in the 1970s, where a growing literature and industry posited that learners have specific, individualized ways of learning that work best for them.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
